 Content
Content
Figures
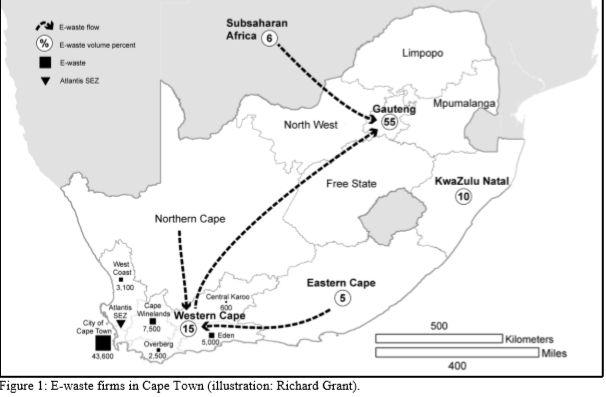
Figure 1: E-waste firms in Cape Town (illustration: Richard Grant).
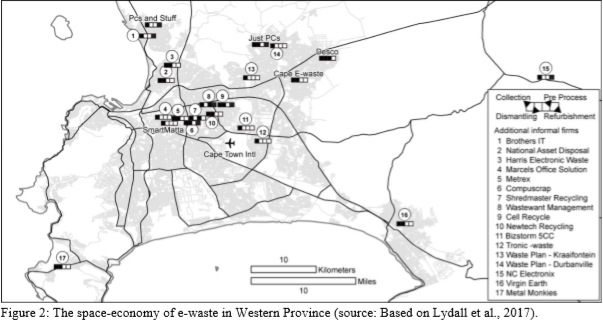
Figure 2: The space-economy of e-waste in Western Province (source: Based on Lydall et al., 2017).
Urbani izziv Volume 30, No. supplement, February 2019
: 5-23
(Articles)
doi: 10.5379/urbani-izziv-en-2019-30-supplement-001
Author
Richard GRANT
Department of Geography, University of Miami, and School of Tourism and Hospitality, University of Johannesburg, South Africa
rgrant@miami.edu
Title
E-waste challenges in Cape Town: Opportunity for the green economy?
Abstract
E-waste research on South Africa cities is modest compared to the much larger research output on other African cities (e.g., Accra, Ghana, and Lagos, Nigeria). Synthesizing gray reports, academic literature, and findings from 25 interviews with key Cape Town stakeholders (from informal and formal firms and industry, civil society, and governmental organizations), this paper assesses the current e-waste landscape in Cape Town, bifurcated between numerous informal individuals/firms and a handful of large formal operators. E-waste activities focus on collection (with little value added), dismantling, preprocessing, and refurbishment without final processing, the latter being performed in Johannesburg and overseas. After a decade of e-waste deliberation, government, businesses, industries, consultants, and civil society organizations are coalescing around approaching e-waste as a strategic green economic opportunity, a tilt coinciding with the designation of Africa’s first designated green special economic zone at Atlantis. The green economy tilt, however, is by no means guaranteed: deficiencies in data, e-waste infrastructure, capacity building, and major differences of opinion about the role of informal operators persist.
Key Words
e-waste, Cape Town, informal economies, green transition